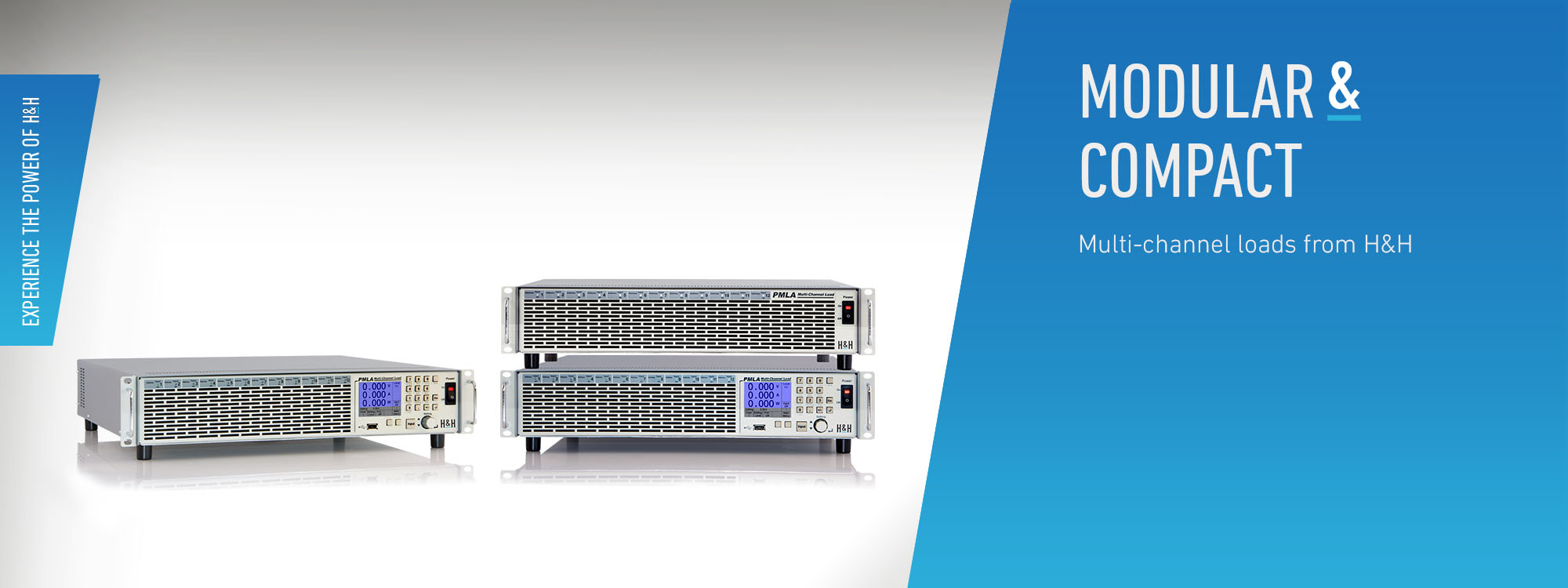

PMLA Series – Multi-Channel Load
Features of performance
Details
Model overview
Downloads
- Configurable multi-channel load ⇒ to the
- Up to 12 channels in 19“ , 2 U
- Tailored configurations possible with modules in 4 voltage and 4 power classes
- 150 W - 300 W - 450 W - 600 W modules
- Input voltages 40 V - 60 V - 120 V - 240 V
- Load currents from 1 A to 120 A
- CC - CV - CR - CP mode
- Dynamic loads
- 1,800 W total power
- Operated via graphical user interface with integrated help system
- SCPI programming with measurement function
- Internal measurement data storage
- Electronic protection
- Analog monitoring outputs for voltage and current
- Analog control input
- Extensive data interfaces
- 19 inch mountable
- Channel expansion via Slave devices
- Trigger system
- MPP tracking
- Discharge function
- Watchdog function
- LabVIEW drivers and software tools available for download
- 2 free calibrations
By loading the video, you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Learn more
Configuration
The PMLA electronic multi-channel load has up to 3 cooling units, each with 4 mounting positions for load modules. 150 W, 300 W, 450 W or 600 W load modules are available. Depending on power, a module occupies one (150 W), two (300 W), three (450 W) or four (600 W) mounting positions.Load Modules
The modules are available in four different voltages 40 V, 60 V, 120 V and 240 V and currents from 1 A up to 120 A. Various loads can be configured, e.g.: 1 x 600 W + 1 x 450 W + 2 x 300 W + 1 x 150 W The total power is max. 1,800 W. The loads can therefore be easily configured to test units with multiple outputs. The load inputs are galvanically separated. Very simple systems can therefore be specially configured for requirements with multi-channel Burn-In equipment.Operating Modes and Functions
The following operating modes are possible:- Current mode
- Voltage mode
- Resistance mode
- Power mode
- Dynamic mode with up to 100 setting values
Measurement Data Storage
A data acquisition function records up to 100 measurement points (time, voltage, current) at each channel and saves it internally.User Interface
The master device has a graphical user interface. All channels, also those of connected slave devices, can be operated.I/O Port
I/O Port for the following functions.- Load setting C and V
- Load on/off
- Voltage monitor output
- Current monitor output
- Sense inputs
Calibration
A free Factory Calibration Certificate (FCC) is supplied with the devices. The calibration process is subject to supervision in accordance with DIN EN ISO 9001. The calibration certificate documents the traceability to national standards to illustrate the physical device in accordance with the international System of Units (SI). Within the 2-year warranty period, we will calibrate a second time free of charge if the respective device (serial number) will have been registrated at H&H.--> Conditions for a second free calibration
For use under laboratory conditions, H&H recommends a calibration interval of 2 years. This is an empirical value that can be used as a guide for the first period of use. Depending on the intended use, service life, relevance of the application and ambient conditions, the operator should adjust this interval accordinglySoftware Tools und Drivers
LabVIEW drivers and software tools are available for download free of charge.Applications
- Calibration of driver outputs
- Consumer test of electrical systems
Test of:
- Batteries and accumulators
- Cables
- Absorbers
- DC/DC converters
- Electronic assemblies
- Electronic fuses and cut-off
- Fuse boxes
- ECUs
- Power distributors
Trigger System
By a trigger system all channels can synchronously be switched on or a programmed waveform can be started.MPP Tracking
The Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) function is used to test solar or photovoltaic modules. For this purpose the maximum power point (MPP) of the connected DUT is controlled by the specific channel.Discharge Function
For testing energy storage devices such as batteries, ultracaps or capacitors, each channel can discharge a connected DUT statically or with defined load profiles up to one or more stop criteria. IUa discharge is also possible, here a constant current is applied until a minimum voltage is reached. This voltage is then kept constant by reducing the current until the current falls below a defined value. Stop criteria are charge, energy, time, current, voltage.Watchdog Function
An adjustable watchdog function may protect the DUT by switching the input off in case of disrupted data communication.Cooler and Load Modules
At each device three cooling units can be installed. At each cooling unit one, two or four modules can be installed, depending on type.Terminals
The load terminals are provided at pluggable terminal strips.Cooling
The air transport from the front panel to the rear panel enables the assembly of compact rack systems without gaps. The temperature-controlled fan control provides a pleasant operating noise.Help System
A help system for most menu items is integrated in the user interface. The help system's language can be set to German or English.Documentation
Each device is supplied with a user manual as PDF file and printed General Safety Instructions, each in German and English.Manuals
Software/Drivers
LoadTerminal_1.1.0.zip
Software tool for transmission of single commands via GPIB/RS-232/Ethernet/CAN
Software tool for transmission of single commands via GPIB/RS-232/Ethernet/CAN

